Business Intelligence Dashboard Software For Data Insights
Business intelligence dashboard software serves as a pivotal tool in today’s data-driven landscape, providing organizations with vital insights through effective data visualization. By consolidating complex data into easily digestible formats, these dashboards empower decision-makers to interpret trends, monitor performance, and strategize effectively. Understanding the importance of these tools is essential for leveraging data to drive business success.
In this exploration, we will delve into the core functions and features that define effective dashboard software, the various types available, and the myriad benefits they offer to organizations. Furthermore, we will address common challenges faced during implementation and share best practices for designing impactful dashboards that enhance decision-making processes.
Introduction to Business Intelligence Dashboard Software
Business intelligence (BI) dashboard software serves as a pivotal tool for organizations to visualize and analyze data effectively. By consolidating disparate data sources into a single interface, these dashboards empower users to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and gain actionable insights, thereby facilitating informed decision-making. As organizations navigate increasingly complex data landscapes, the importance of robust BI dashboard software cannot be overstated.The primary functions of business intelligence dashboard software include data aggregation, real-time monitoring, and performance tracking.
These features enable users to create intuitive visual representations of data, such as graphs, charts, and tables, which can simplify the interpretation of complex datasets. Effective dashboard software should also offer customization options, allowing organizations to tailor the visualizations to meet specific business needs. Furthermore, the integration of advanced analytics capabilities, such as predictive modeling and trend analysis, enhances the decision-making process, enabling organizations to anticipate future challenges and opportunities.
Core Features of Effective Dashboard Software
The effectiveness of business intelligence dashboard software hinges on several core features, each contributing to the overall functionality and user experience. These features include:
- Data Integration: The ability to connect and aggregate data from multiple sources, including databases, cloud services, and third-party applications, is critical for comprehensive analysis.
- User-Friendly Interface: A well-designed interface, complete with drag-and-drop functionalities, simplifies the process of creating and customizing dashboard elements, making it accessible to users with varying technical skills.
- Real-Time Data Updates: Dashboards that provide real-time updates ensure that users are working with the most current information, which is essential for timely decision-making.
- Customizable Visualizations: The option to tailor visualizations based on user preferences and organizational needs enhances the relevance and effectiveness of data presentations.
- Collaboration Tools: Features that facilitate sharing insights and reports among team members foster a collaborative environment, enabling collective decision-making.
- Mobile Accessibility: The ability to access dashboards on mobile devices allows decision-makers to stay informed and respond promptly, regardless of their location.
The significance of these features becomes apparent when considering the role of dashboards in decision-making processes. Dashboards act as a central hub for monitoring business performance, allowing stakeholders to identify trends, track progress against goals, and recognize areas that require attention or improvement. By visualizing data effectively, organizations can make informed decisions that drive growth and enhance operational efficiency.
“The use of business intelligence dashboards transforms raw data into strategic insight, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions with confidence.”
Incorporating effective BI dashboard software into organizational practices not only enhances data visibility but also fosters a culture of transparency and accountability, ultimately contributing to an organization’s long-term success.
Key Features of Effective Dashboard Software
Effective dashboard software serves as a crucial tool for organizations seeking to harness data for better decision-making. The primary goal of these dashboards is to provide a clear, concise visual representation of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that inform strategic initiatives. A well-designed dashboard should facilitate data-driven insights, and its effectiveness hinges on several key features.Understanding the essential features of dashboard software helps organizations select the right tools to meet their business needs.
Key elements such as data integration, real-time monitoring, and user-friendly interfaces are critical in ensuring that the dashboard delivers the intended value. These features work together to enhance usability and effectiveness, enabling users to gain insights swiftly and accurately.
Essential Features of Dashboard Software
The following features are vital for any effective dashboard software. Each feature plays a significant role in optimizing the user experience and ensuring that actionable insights are readily accessible.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Examples of Software |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Integration | Ability to connect various data sources, including databases, APIs, and external applications. | Provides a holistic view of data, enabling comprehensive analysis. | Tableau, Power BI |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Updates data continuously, allowing users to see live changes and trends. | Facilitates timely decision-making based on the most current information. | Google Data Studio, Klipfolio |
| User-Friendly Interface | Intuitive design that enhances user experience and accessibility. | Reduces the learning curve and increases user engagement. | Looker, Domo |
| Customization Options | Ability to personalize dashboards through widgets, themes, and layout changes. | Allows users to tailor the dashboard to their specific needs and preferences. | Qlik Sense, Sisense |
Dashboard software such as Tableau is renowned for its robust data integration capabilities, allowing users to pull data from a multitude of sources seamlessly. On the other hand, Google Data Studio excels in real-time monitoring, providing users with live data updates that enhance decision-making processes. Additionally, software like Looker stands out for its user-friendly interface, making it accessible for users at all proficiency levels to create insightful visualizations easily.
By leveraging these features, organizations can ensure that their dashboard software meets the demands of today’s data-driven environment effectively.
Types of Business Intelligence Dashboard Software
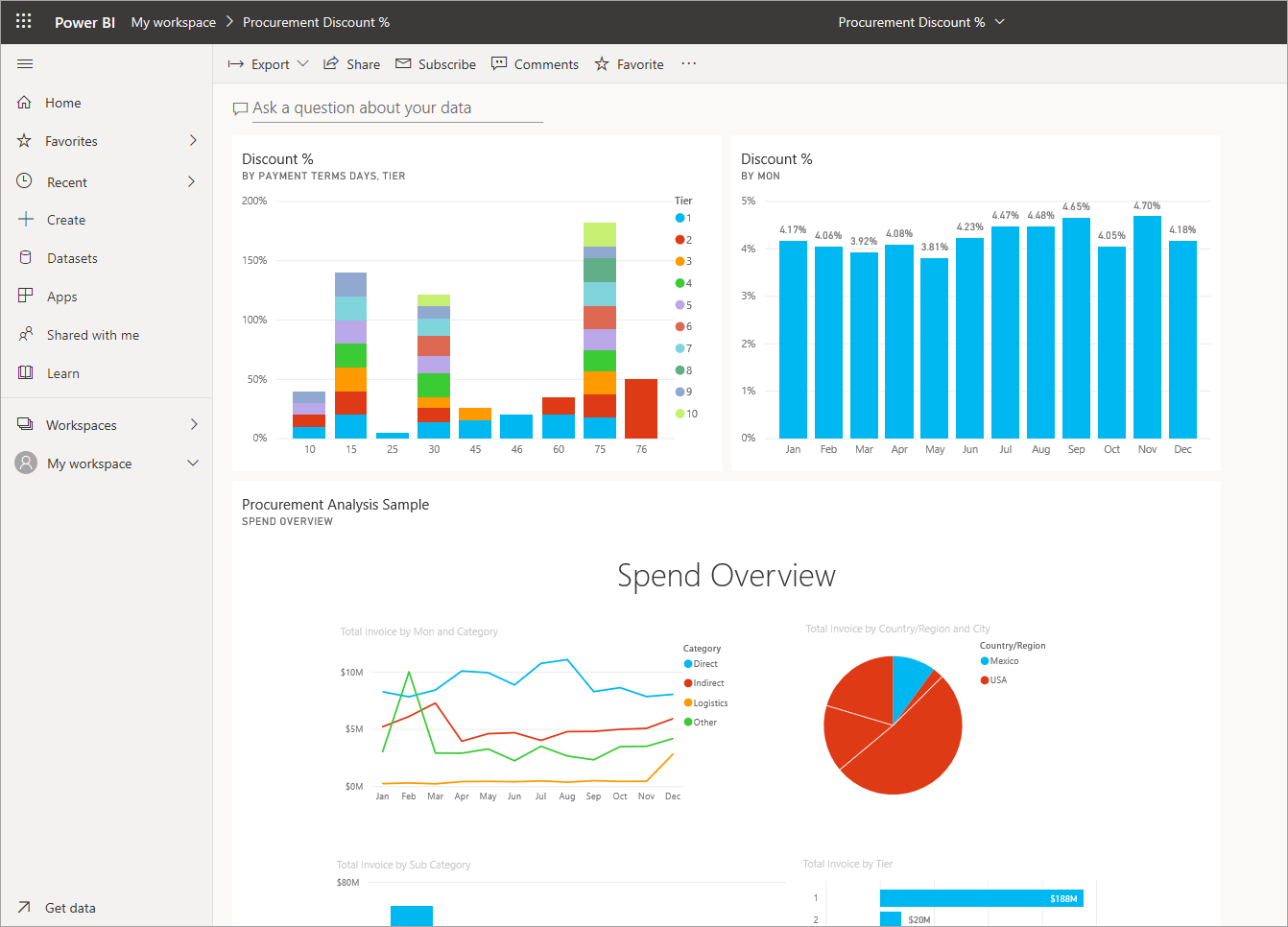
Business Intelligence (BI) dashboard software can be categorized into three primary types: operational, strategic, and analytical dashboards. Each type serves distinct purposes and is designed to meet varying business needs, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on different data perspectives. Understanding these categories is essential for selecting the right dashboard that aligns with specific organizational goals.Operational dashboards are designed for real-time monitoring of business operations.
They provide an overview of day-to-day activities and key performance indicators (KPIs), allowing teams to react promptly to any operational anomalies. These dashboards focus on immediate data that can assist in decision-making processes on the ground.Strategic dashboards, in contrast, are aimed at senior management and executives. They provide a broader view of the organization’s performance over time, focusing on long-term goals and trends.
These dashboards typically aggregate data from various operational systems to present a high-level overview of organizational performance, which aids in strategic planning and decision-making.Analytical dashboards offer a deeper level of data analysis, enabling users to explore complex datasets and uncover insights through advanced analytics. These dashboards are primarily used by data analysts and business intelligence professionals, providing tools for detailed data exploration, trend analysis, and predictive modeling.
Comparison of Dashboard Types
Understanding the distinctive attributes of each type of dashboard software aids organizations in choosing the right solution to meet their needs. The following comparison chart Artikels key functionalities and use cases for operational, strategic, and analytical dashboards:
| Type of Dashboard | Primary Functionality | Target Audience | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational | Real-time monitoring of daily operations | Operational teams, managers | Monitoring sales performance, customer service metrics, inventory levels |
| Strategic | Overview of long-term organizational performance | Executives, senior management | Tracking quarterly revenue trends, market share analysis |
| Analytical | In-depth data analysis and exploration | Data analysts, business intelligence professionals | Forecasting sales, identifying customer behavior patterns |
“Each type of dashboard serves a unique purpose and audience, emphasizing the importance of aligning your dashboard choice with specific organizational needs.”
Benefits of Using Business Intelligence Dashboards: Business Intelligence Dashboard Software
The implementation of business intelligence dashboards provides organizations with a multitude of advantages that significantly enhance decision-making processes and operational efficiency. These tools serve as a centralized platform for data visualization, enabling users to access critical insights quickly and intuitively. By leveraging dashboard software, businesses can transform raw data into actionable information, leading to more informed strategies and improved performance.One of the primary benefits is improved data accessibility.
Dashboards consolidate data from various sources into a single interface, making it easier for stakeholders to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time. This level of accessibility allows teams to respond promptly to trends and anomalies, thus fostering a proactive approach to management. Furthermore, enhanced reporting capabilities streamline the communication of complex data insights, allowing for clearer presentations to clients and stakeholders.
Case Studies of Business Intelligence Dashboard Impact
Numerous organizations have experienced substantial benefits from implementing business intelligence dashboards. For instance, a retail chain utilized dashboard software to integrate sales data from multiple locations. This initiative led to a 20% increase in sales within six months, as store managers could identify successful trends and replicate strategies across branches. Another notable success story involves a healthcare provider that adopted a dashboard solution to monitor patient care metrics.
By visualizing patient flow and resource allocation, the organization improved its operational efficiency, resulting in reduced wait times and enhanced patient satisfaction ratings.
Metrics Effectively Tracked Using Business Intelligence Dashboards, Business intelligence dashboard software
To maximize the effectiveness of business intelligence dashboards, organizations can track a variety of metrics that reflect performance across different domains. The selection of relevant metrics is critical to ensure that the insights gained are actionable and aligned with organizational goals. The following list highlights key metrics that can be effectively monitored:
- Sales performance metrics, including total sales, sales growth rate, and average transaction value
- Customer satisfaction scores, such as Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
- Operational efficiency indicators, including average processing time and resource utilization rates
- Financial metrics, such as gross profit margin, net profit margin, and return on investment (ROI)
- Marketing performance metrics, including conversion rates, click-through rates (CTR), and cost per acquisition (CPA)
The effective tracking of these metrics enables organizations to make data-driven decisions that enhance overall performance. Each metric provides valuable insights into different facets of the business, allowing for continuous improvement and strategic planning.
Challenges in Implementing Dashboard Software
The adoption of dashboard software can significantly enhance an organization’s data visualization and decision-making capabilities. However, several challenges often arise during the implementation process that can hinder its effectiveness. Understanding these hurdles is crucial for organizations aiming to successfully integrate dashboard software into their operations.One of the predominant challenges faced by organizations is the resistance to change among employees. This reluctance can stem from a lack of familiarity with new technologies or fear of the unknown.
Additionally, organizations may struggle with data quality and integration issues, particularly if existing data systems are disjointed or poorly maintained. Furthermore, there is often a lack of clear objectives for what the dashboard should achieve, leading to misaligned expectations and ineffective usage.
Best Practices for Overcoming Implementation Challenges
To address these challenges and facilitate a smooth implementation process, organizations can adopt several best practices:
Engage Stakeholders Early
Involve key stakeholders from various departments during the planning stages to ensure their needs are considered, fostering a sense of ownership.
Provide Comprehensive Training
Offer training sessions tailored to different user levels, ensuring that all employees understand how to utilize the dashboard effectively.
Define Clear Objectives
Establish specific goals for the dashboard to align its functionalities with business needs, making it easier to measure its success post-implementation.
Focus on Data Quality
Prioritize the cleansing and integration of data from various sources to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information displayed on the dashboard.
Iterate Based on Feedback
Launch the dashboard in phases and gather user feedback to make necessary adjustments, ensuring continual improvement and user satisfaction.
Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
While dashboard software can be highly beneficial, it also poses certain risks that organizations should be aware of. Understanding these risks and implementing mitigation strategies can help maximize the software’s effectiveness. The following points highlight these risks and their corresponding mitigation measures:
Risk of Data Overload
Dashboards can become cluttered with excessive data, leading to user confusion.
*Mitigation*
Simplify dashboard designs and focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) that matter most to the organization.
Inaccurate Data Representation
Poorly managed data can result in misleading insights.
*Mitigation*
Regularly audit data sources and establish robust data governance practices.
User Resistance
Employees may resist using the dashboard due to a lack of understanding or perceived complexity.
*Mitigation*
Implement user-friendly interfaces and provide ongoing support and training to encourage adoption.
Inconsistent Updates
Stale or outdated data can undermine the dashboard’s value.
*Mitigation*
Automate data updates where possible and establish routine check-ins to ensure data relevance.
Limited User Engagement
Users may not engage with the dashboard if it doesn’t meet their needs.
*Mitigation*
Encourage user feedback to make iterative improvements and involve users in the design process.By recognizing these challenges and adopting strategic best practices, organizations can enhance their chances of successful dashboard software implementation, leading to improved data-driven decision-making and overall business performance.
Best Practices for Designing Effective Dashboards

Designing an effective dashboard is crucial for successful data communication and decision-making. An intuitive dashboard not only presents data insights clearly but also enhances user engagement and facilitates informed actions. This section Artikels best practices for creating dashboards that convey essential information efficiently.
Designing Intuitive Dashboards
An intuitive dashboard allows users to understand data at a glance, fostering quick decision-making. Key elements include:
Clarity of Purpose
Each dashboard should have a defined objective, ensuring that the displayed metrics align with user goals. For instance, a sales dashboard should focus on revenue, conversion rates, and sales trends rather than irrelevant data points.
Logical Layout
The arrangement of visual elements should follow a logical flow, grouping related information together. A common practice is placing the most critical insights at the top or in a prominent position, ensuring they catch the user’s eye first.
Minimalism
Avoid clutter by limiting the number of visuals and focusing on essential metrics. This approach reduces cognitive load and enables users to quickly absorb the information presented.
Selecting the Right Visualizations
Choosing appropriate visualizations is vital for accurately representing data and enhancing user comprehension. Different types of data require specific visualization techniques:
Bar Charts
Ideal for comparing discrete categories, such as sales by region.
Line Graphs
Effective for showing trends over time, such as monthly revenue growth.
Pie Charts
Useful for illustrating parts of a whole, such as market share distribution.
Heat Maps
Suitable for displaying data density across a geographical area, such as customer locations. Selecting the right visualization improves the interpretability of the data, making critical insights more accessible.
Essential Design Principles Checklist
Following a set of design principles can enhance dashboard effectiveness. Consider the following checklist when creating dashboards:
Consistency in Design
Use uniform colors, fonts, and styles across all dashboard elements to maintain a cohesive look.
Color Choice
Utilize color strategically to draw attention to important metrics but avoid overwhelming users with excessive color variations. Color-blind friendly palettes are also recommended.
Responsive Design
Ensure the dashboard is accessible across various devices and screen sizes, accommodating users who may access the dashboard from mobile devices.
Tooltips and Annotations
Provide contextual information through tooltips and annotations to clarify data points without cluttering the dashboard.
User Feedback
Incorporate user feedback during the design process to ensure that the dashboard meets the needs of its intended audience.By adhering to these best practices, dashboard designers can create effective tools that empower users to derive meaningful insights from their data.
Future Trends in Business Intelligence Dashboard Software
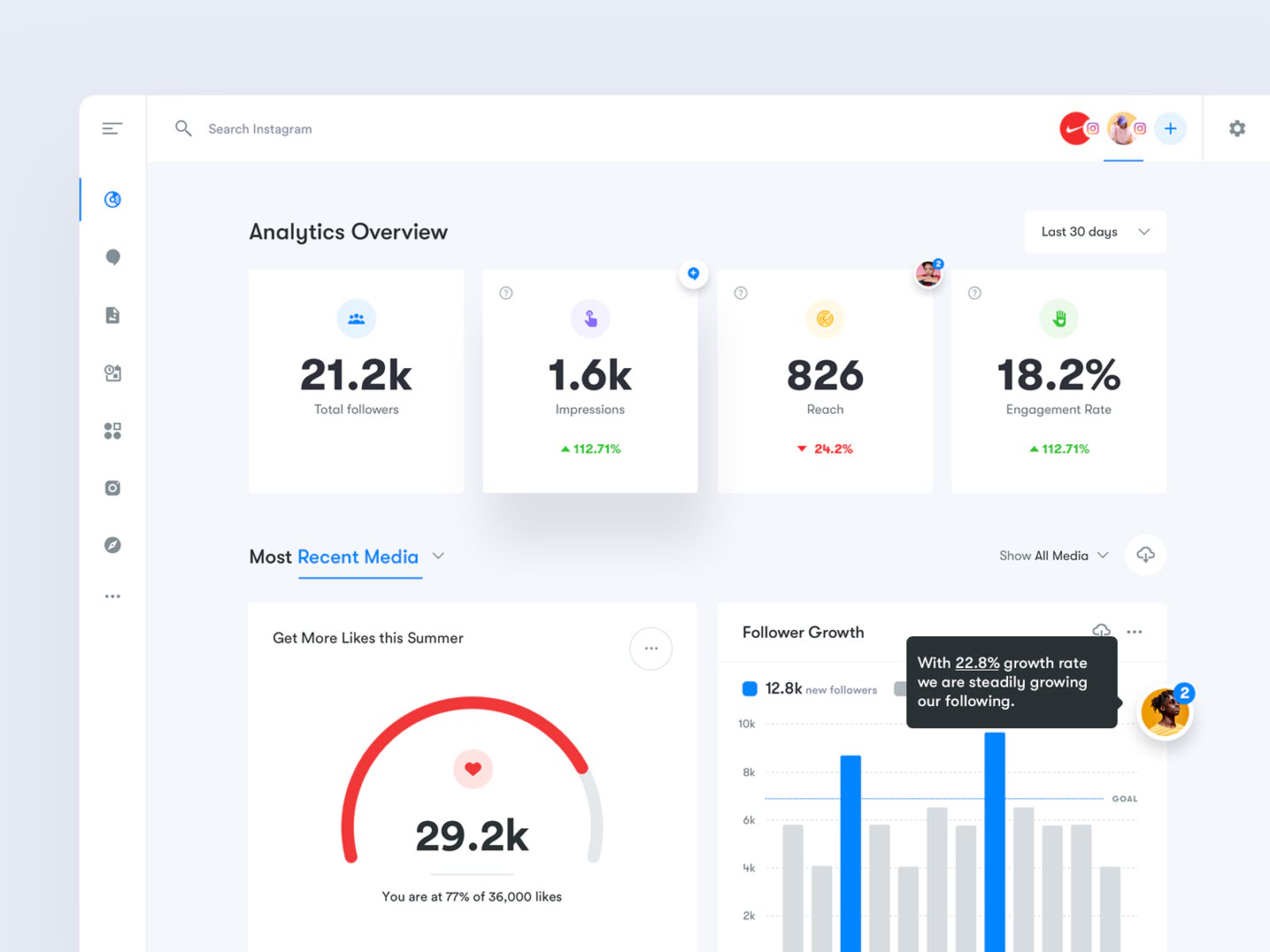
The landscape of Business Intelligence (BI) dashboard software is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing business needs. As organizations increasingly rely on data to make informed decisions, the future of dashboard software promises a host of innovative features and capabilities designed to enhance user experience and analytical power.Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and advanced data visualization techniques are significantly shaping the future of dashboard software.
These innovations are set to redefine how users interact with data, enabling more intuitive and personalized experiences. Furthermore, the integration of real-time data processing capabilities will allow organizations to respond swiftly to changing market conditions.
Key Emerging Technologies Influencing Dashboard Software
A variety of emerging technologies are expected to play pivotal roles in future dashboard software development. The following points summarize some of the most significant trends:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML algorithms will facilitate automated insights, predictive analytics, and personalized dashboard experiences by learning from user behavior and preferences.
- Natural Language Processing: This technology will enable users to interact with dashboards using conversational queries, making data analysis more accessible to non-technical users.
- Augmented Analytics: By automating data preparation and insight generation, augmented analytics will streamline the analytical process, allowing users to focus on data interpretation.
- Integration with IoT Devices: The ability to visualize data from IoT devices in real time will enhance decision-making processes across various industries.
- Enhanced Data Storytelling: Advanced visualization tools and techniques will help users create compelling narratives from their data, facilitating better communication of insights.
Potential Standard Features in Next-Gen Dashboard Tools
As the BI market continues to mature, certain features are likely to become standard in the next generation of dashboard tools. The following elements will enhance functionality and usability:
- Real-Time Data Updates: Dashboards will increasingly provide real-time insights, allowing businesses to make timely decisions based on the most current information available.
- Customizable User Interfaces: Future dashboard solutions will offer extensive customization options to adapt to different user needs and preferences, ensuring a more personalized experience.
- Mobile Accessibility: As mobile computing gains traction, dashboards will be designed for seamless access across devices, enabling users to view and interact with data on-the-go.
- Collaboration Tools: Enhanced sharing and collaboration features will facilitate teamwork and communication among users, making it easier to make data-driven decisions collectively.
- Data Governance Features: As data privacy concerns grow, dashboards will incorporate robust governance capabilities to ensure compliance and maintain data integrity.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning on Dashboard Functionalities
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are set to revolutionize dashboard functionalities, offering unprecedented capabilities that enhance user experience. The integration of these technologies allows for several impactful applications:
- Automated Insights: AI-powered analytics can automatically highlight critical trends and anomalies in data, providing users with actionable insights without requiring extensive manual analysis.
- Predictive Analytics: ML algorithms can analyze historical data to identify patterns and predict future outcomes, enabling proactive decision-making.
- Personalized Recommendations: By learning from individual user interactions, AI can tailor recommendations and insights, improving the relevance of the information presented.
- Enhanced Visualizations: AI can drive the development of dynamic visualizations that adapt based on user queries or data changes, making complex information more digestible.
- Self-Service Analytics: AI-driven dashboards will empower users to conduct their analyses independently, reducing reliance on IT teams and fostering a data-driven culture.
Common Queries
What is business intelligence dashboard software?
It refers to software tools that aggregate, visualize, and analyze data from various sources to help organizations make informed decisions.
How does dashboard software improve decision-making?
By providing real-time data visualization and insights, it allows decision-makers to quickly identify trends and make data-driven choices.
What types of data can be displayed on a dashboard?
A dashboard can display various types of data, including sales figures, customer metrics, performance indicators, and operational statistics.
Are there any risks associated with using dashboard software?
Yes, potential risks include data misinterpretation, over-reliance on visuals without context, and security vulnerabilities if not properly implemented.
How can organizations ensure successful implementation of dashboard software?
By following best practices such as user training, setting clear objectives, and ongoing support, organizations can enhance the effectiveness of their dashboard implementations.